The Underworld: Journeys to the Depths of the Ocean (Susan Casey) is an interesting book about privatized and recreationalized (is that a word? ) deep submarine excursions. The book seems to have been written before the Titan imploded near the Titanic (June 2023) and then published shortly after the tragedy.
This is more about the personalities and feelings of deep-sea exploration, but there is enough engineering background and detail to make it interesting for the quantitative reader. It is good background for understanding the psychology of the people who built and dove on the Titan.
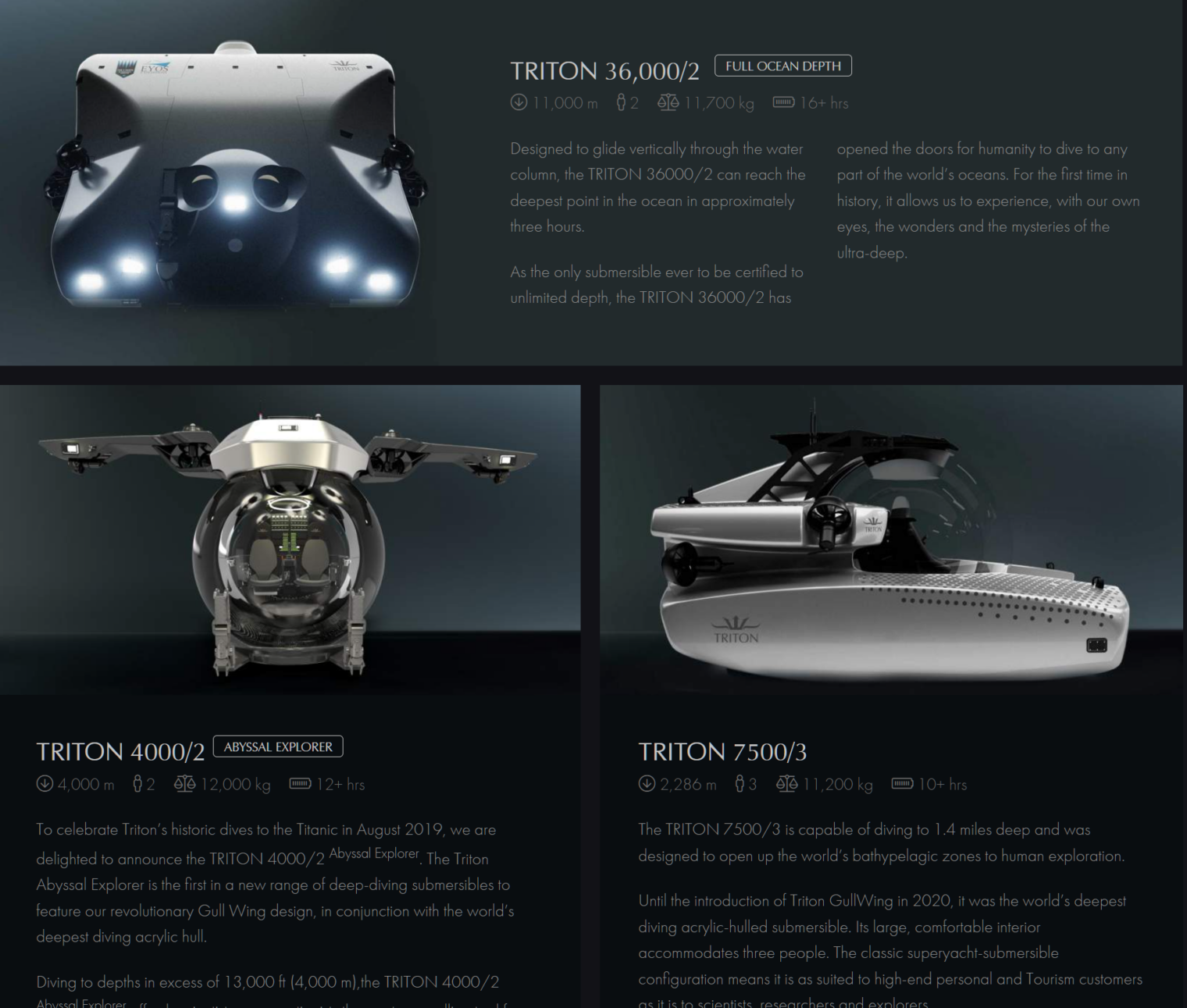
In 2007, [Patrick] Lahey had cofounded Triton Submarines [of Sebastian, Florida] to create a new generation of eye-catching, user-friendly subs, with acrylic spheres, decent headroom, and plush leather seats. Their maximum depths didn’t extend beyond the twilight zone, but that was deep enough for a taste of the sublime. The subs were a hit with yacht owners—and with filmmakers and scientists, who reveled in the immersive visual experience.
When the hedge fund magnate Ray Dalio loaned his Triton sub to a group of marine biologists in 2012, they captured the first footage of a giant squid hunting off Japan. Previous encounters with the animal had meant ogling a dull mauve corpse: before that dive, nobody had ever witnessed a giant squid in action. The scientists were stunned, because far from being blandly colored, the massive creature looked metallic, as though it had been dipped in silver and bronze. It moved with the fluidity of water itself, its long tentacles studded with suckers, its hubcap eye gazing directly at the camera.
How many more epiphanies were down there? A good rule of thumb is the deeper you go, the stranger things get—and now Lahey had mobilized his decades of experience to build a sub that could explore the deepest reaches of the underworld. As far back as 2011, Triton’s website had included a mockup of the 36000/3, a sub that would take three people to thirty-six thousand feet, or full ocean depth. But this dream machine existed only in pixels: no vehicle was headed to Hades unless someone with a burning desire to dive below twenty thousand feet stepped up to write a series of seven-figure checks. And extremely wealthy people who want to be sealed inside a metal ball and sent plummeting for miles into the ocean’s sepulchral blackness are not found on every street corner.
Once Triton existed anyone with a some cash to spare could launch the kinds of expeditions that previously only governments could undertake.
The saddest part of the history section:
Deep-sea submersibles are an inherently risky proposition, but the field has a sterling safety record. No one has died in a manned submersible since 1974, when an electrical fire inside a Japanese craft caused the two-man crew to be overcome by toxic fumes.
There is plenty of risk and failure is always an option:
Of the many ways a pilot can find himself in trouble beneath the ocean’s surface, the biggest risk is entanglement: getting snagged on fishing gear, cables, debris, or even ropes. There is no plan B when you’re stuck a mile down. Somehow the sub must be freed. “I’ve been hung up twice,” Kerby said, looking sober. The first time happened early in his career. “I was a green pilot, and I got caught in the lines from a shrimp trap. And I knew that if I couldn’t get out of it, I would die.” The second entanglement was more recent: Kerby ran into a pile of cable that had been dumped by a tugboat. “The worst thing you can do is thrash around,” he said. “You have to stop and take stock of your heading, and try to project yourself outside of the sub.” Both times, he added, it took hours of dressage-style maneuvering to escape. “Self-help is the only help, that’s our motto.”
The Pisces are equipped with five days of life support, so anyone marooned underwater would have plenty of time to consider their fragile mortality. This wasn’t a theoretical situation. In 1973, another Pisces submersible, the Pisces III, suffered a hatch failure that flooded its external machinery tank, overburdening the sub and causing it to plummet to the North Atlantic seafloor with its two pilots trapped inside the pressure hull.
Thankfully, the Pisces III crashed on soft bottom mud without catastrophic damage, at a depth of 1,575 feet—shallow enough to attempt a rescue. (It narrowly avoided falling over a shelf that would’ve carried it beyond reach.) That was the good news. The bad news was that submarine rescues are logistically complicated scrambles that often fail to beat the mercilessly ticking clock.
The Pisces V—at the time owned by a Canadian company and working in British Columbia—was airlifted to the scene, along with the Pisces II, which had been laying cable in the North Sea. While the stranded pilots, Roger Chapman and Roger Mallinson, endured this long wait, they watched the Pisces III’s oxygen supply dwindling like an hourglass. Hypothermia set in, then dehydration, then delirium from breathing too much carbon dioxide. Terrible weather and plain bad luck slowed the rescue, but finally the other subs were able to attach lines to the Pisces III. By the time Chapman and Mallinson were craned to the surface, they’d been in the sphere for eighty-four hours. Only twenty minutes of oxygen had remained in their tanks.
The book also contains a story of nonprofit org fraud and startup fraud:
Since the International Seabed Authority opened its doors in 1994, its 168 members (now numbering 168 delegates from 167 nations and the European Union) have met annually at its headquarters in Jamaica to prepare for the biggest resource haul the world has ever known—or as one marine scientist put it, “the greatest assault on deep-sea ecosystems ever inflicted by humans.”
To date, the ISA has granted thirty-one mining exploration contracts covering about six hundred thousand square miles, a seabed footprint the size of Alaska. Nineteen of those contracts are for nodule mining, but with an expansiveness that would have delighted Mero, the other twelve contracts would allow miners to investigate scalping the tops off seamounts and grinding up hydrothermal vents. Apparently it’s not hard to get an exploration contract, because so far the ISA has approved every application. Any member state that pays a $500,000 fee and follows procedure can soon have exclusive rights to its own patch of seabed. There’s no stinting on size: an average CCZ contract area spans about thirty thousand square miles. Some nations already hold multiple contracts (China has five) and there’s nothing to prevent any ISA member state from obtaining more, usually by sponsoring contracts on behalf of private-sector mining companies. (In that case, the mining company puts up the capital, runs the show, and would pocket most of the profits—theoretically, billions. The sponsoring nation receives a small royalty, and could be liable for damages if anything goes wrong.) Ultimately the ISA stands to benefit from every contract it grants, with royalties rolling in from each mining operation. Some of that cash will be distributed to developing nations, but a portion flows to the ISA itself—a jarring conflict of interest for a group that also serves as the industry’s regulator. Absurdly, there are even plans for the ISA to develop its own nodule mining concession called “the Enterprise.”
Then add some credulous environmentally conscious investors…
The story got bigger: DeepGreen’s pursuit of nodules was about nothing less than saving the world. And [Gerard] Barron was everywhere, telling it at length. It was a blur of land-based mining destroying rain forests Africa child labor toxic tailings fossil fuel human rights violations versus renewable energy closed-loop recycling no-waste sustainable abundant nodules that “literally lie on the ocean floor like golf balls on a driving range.” “I’m doing this for the planet and the planet’s children,” Barron said. Also, for an 8.1 percent stake in a company that would soon be listed on the NASDAQ. In 2021, DeepGreen went public in a SPAC merger, changing its name to the Metals Company (ticker symbol: TMC). It was valued at $2.9 billion, which was impressive given that it had no revenue, and its only assets were seabed rights that supposedly belong to the rest of us.
The TMC stock debuted at $11.05 a share, spiked to $15.39, and fell to $3.48 within a month. (It has since dropped below a dollar.) Accounting problems emerged; lawsuits followed. Shareholders joined a class-action suit, alleging the Metals Company had made “materially false and misleading statements”;
The Explorers Club in New York City is full of members not afraid to risk anything… except SARS-CoV-2 infection:
The Madagascar hissing cockroaches were roasted extra-crispy, glistening on wooden skewers. They were bigger and shinier than the Costa Rican cave cockroaches and the Argentinian wood cockroaches, with longer antennae and a formidable set of horns. If you were hoping for a black-tie occasion to sample a variety of roaches, this was the only game in town: the 118th Explorers Club Annual Dinner. Archaeologists, anthropologists, geologists, field biologists, polar explorers, marine scientists, endurance athletes, space travelers, wildlife photographers, ocean conservationists, extreme climbers, single-handed sailors, and assorted peers: this was their party, a global gathering of adventurers. For the last two years, the annual dinner had been canceled due to COVID, so the night was both a reunion and a celebration, the rooms overflowing with the club’s members and guests.
More: read The Underworld: Journeys to the Depths of the Ocean
Full post, including comments