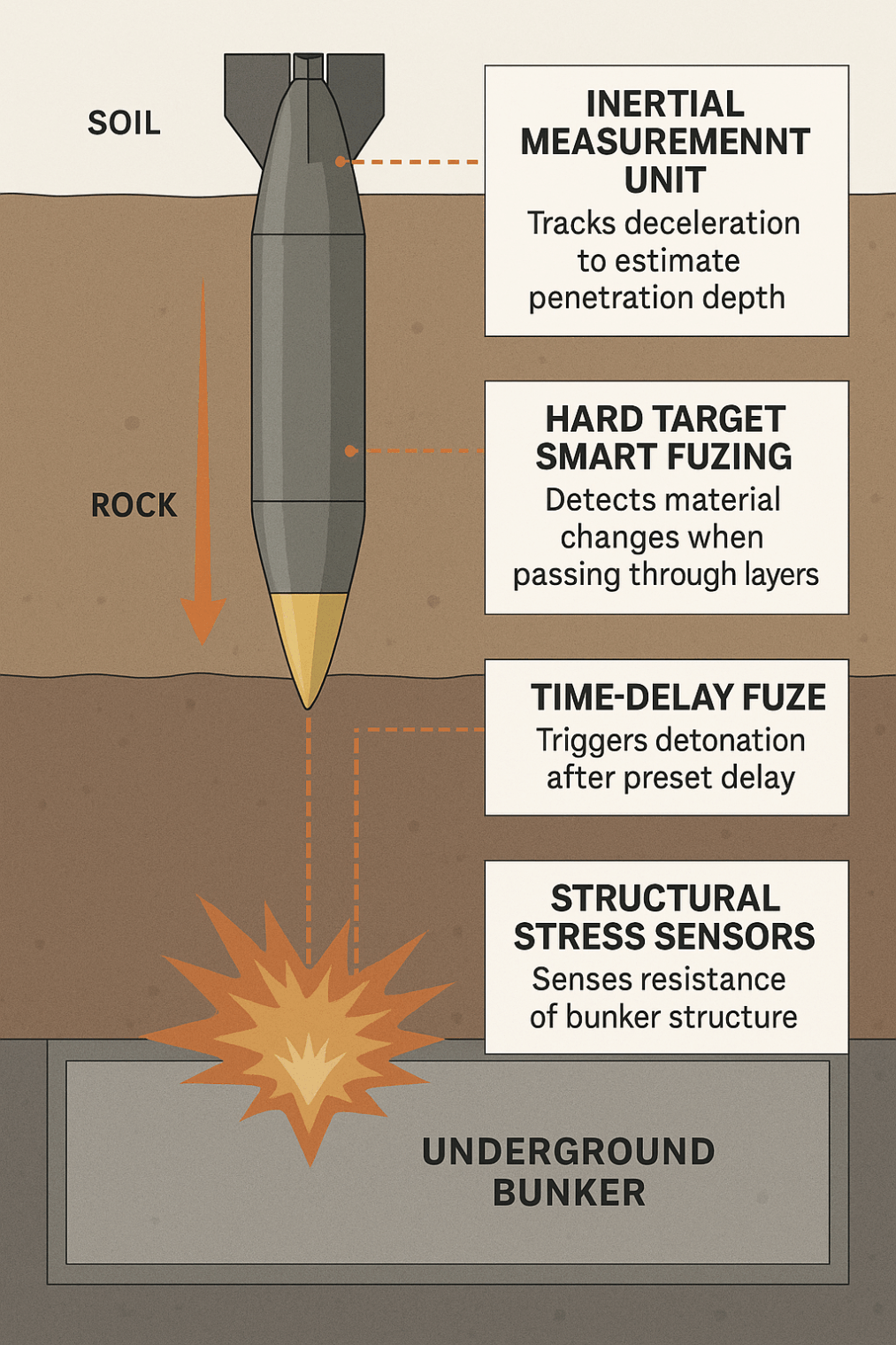
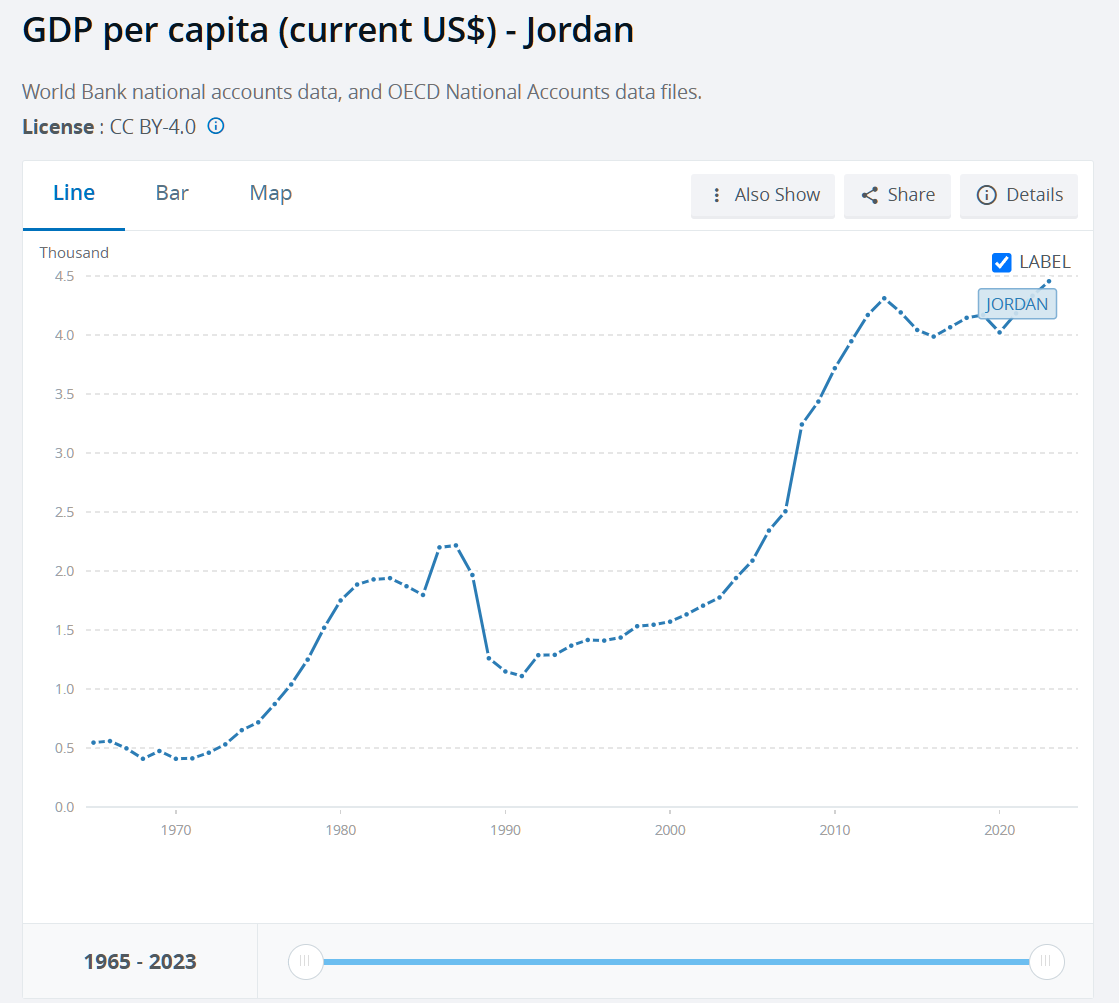
I’m been reading The Battle of Manila: Poisoned Victory in the Pacific War (Nicholas Evan Sarantakes, a professor at the U.S. Naval War College; published 2025 by Oxford University Press (i.e., a military work from a publisher in a country that can’t defend its own border)).
The loss of the Philippines in the first place was due to incompetence, similar to how Japanese success at Pearl Harbor was due to incompetence (failure to heed a radar warning of planes inbound from the NW). Having squeezed and provoked Japan, the U.S. expected attacks in Asia and yet the Japanese caught the Americans by surprise:
Recalled to active duty as the United States was on the verge of war, MacArthur wanted to defend the entire archipelago. “We are going to make it so very expensive for any nation to attack these islands that no one will try it,” he explained. On the first day of the war, the Japanese caught the air forces under his command on the ground and destroyed them. MacArthur then attempted to defend the entire island of Luzon. While his men did well tactically—fighting the Japanese to a standstill—their supplies were in the wrong positions, which sealed their fate as they retreated into the cul-de-sac that was the Bataan Peninsula.
The decision to fight in 1945 to take back the Philippines might also be said to have been an example of American military incompetence. Most of the senior officers wanted to ignore the Philippines and capture Formosa (present-day Taiwan) instead as a more useful base for bombing and invading Japan (USNI article). The Philippines would have been freed from Japanese rule in August 1945 when Japan unconditionally surrendered, though of course it was tough to know that in late 1944.
The book is about the fight for one city, Manila, and as such there are some parallels to the present-day fighting in Gaza. What the two battles have in common:
- a mostly urban environment
- the majority of people in the environment were/are not soldiers
- the army trying to take the city (US in 1945; IDF today) was trying to minimize the number of non-soldiers killed
- the army defending the city was indifferent to the number of non-soldiers killed and/or actually trying to increase the number of non-soldiers killed
The differences:
- the non-soldiers of Manila were hostile to the defending army (Japan) and, in fact, was an organized guerilla force against the army whereas the non-soldiers of Gaza are fervent supporters of the defending army
- the army attacking Manila (US) was trying to minimize damage to buildings and other infrastructure
- the army attacking Manila (US) wasn’t trying to feed the army defending Manila (Japan) and, in many cases, defenders had to surrender or commit suicide because they’d run out of food and/or water
The book reminds us that war is most glorious when seen in the rearview mirror:
One of the great myths of World War II is that the American public immediately rallied to the cause after Pearl Harbor. The truth is that men had to be drafted, and they did not want to be in either the Army or the Philippines. Willard Higdon was honest about his motivations: “I was 27 yrs old, with a wife and a 5 yr. old dtr. I did not want to go.”
The Japanese actually weren’t that excited about owning the Philippines:
The main reason for their invasion in 1941 and 1942 was geopolitical. The Philippines had few natural resources that the Japanese economy required. What they wanted was to drive the Americans out of the western Pacific and, once that was done, they wanted to liquidate their commitment to the Philippines quickly. The Japanese had little interest in turning the archipelago into a Japanese colony.
The enemy doesn’t always cooperate with one’s plans…
Even as late as February 5 [the battle was February 3-March 3], MacArthur had no plan for an urban battle. “I do not believe anybody expected the Japs to make a house-to-house defense of Manila,” Eichelberger told his wife. The general belief—at MacArthur’s headquarters, at Krueger’s headquarters, and with the press—was that the Japanese would evacuate without a fight. Thirty years later, when he sat down to write his memoirs, Chase could not understand why anyone had made this assumption. “It was counter to everything the Nips had done in previous campaigns.”
The U.S. had almost no experience with the kind of fighting that was to ensue:
Other than some short operations in World War I and a few in the European theater, the last time Americans had fought in cities had been in 1864 and 1865 with the battles of Atlanta and Richmond. There are seven major characteristics of urban warfare. The first is that artificial terrain features constrain and channel movement. Buildings become significant geographical objectives. Roads direct advances in certain directions. Both can be barriers. Depending on the material used in their construction, they might be quite vulnerable to military action or quite impervious. Some weapons have better utility than others in the city, and these issues often influence tactics. Another feature is that ground operations are compressed and decentralized. Engagements are between small, tactical units—squads, platoons, companies—for small, geographic objects—a room, a building, or a city block. A third factor is that combat usually becomes three-dimensional. Soldiers fight ground operations as in any other form of ground combat, but they also advance and fight in sewers and blast holes through basement walls. They also have to fight an opponent that might control the floor of a building immediately above or below them, and they might move from rooftop to rooftop. City combat always consumes more time than other forms of fighting. This factor is relative, though. How slow is slow? The month-long fight for Manila was significant compared to other ground operations fought in the Pacific, but nothing compared to the eight-month-long struggle for Stalingrad or the twenty-eight-month-long siege of Leningrad. A fifth factor in urban warfare is the presence of civilians. There are always non-combatant deaths in urban operations and their presence requires some effort at stability operations afterward, but sometimes also during the period of active combat. Civilians can be assets or liabilities when it comes to intelligence gathering, as both the Americans and Japanese would learn. The ready influence of the media is another factor. Cities by their very nature are media centers and always have resident journalists. Since urban areas are also important population, political, economic, financial, cultural, religious, trade, and transportation centers, their fate attracts the interest of reporters. A final dynamic of urban warfare is the outsized ramification of its outcomes. Location matters, and cities are always more important than undeveloped countryside, and engagements for their control have more influence than engagements in isolated areas. Each of these would be in play in Manila.
As in the Gaza fighting, the army trying to take the city owns the airspace:
The US forces also had total air superiority, and piper cub observation planes loitered over the city looking for targets.
(Note failure to capitalize Piper Cub!)
A civilian population that does not support the defending army makes a city tough to defend:
The Japanese were well aware that the Filipinos on Luzon were welcoming the Americans enthusiastically. They resented this and they had orders—which they implemented willingly—to make the Manileños pay. The Battle of Manila was defined by the methodical targeting of the civilian population. The Japanese historian Hayashi Hirofumi has argued, given where most of the incidents took place, that the majority of these killings were done by the Imperial Japanese Army.1 Their orders, though, came from Rear Admiral Iwabuchi Sanji. He made the determination that there was no difference between Filipino guerrillas and civilians. “When the enemy invaded Manila, the citizens were welcoming the enemy well and disrupted all of our fighting action,” he reported. “The number of citizens is estimated to be about seven hundred thousand, but on the front line north of the Pasig River between 3 and 5 February, the general public carried out the following guerrilla activities: communicate with U.S. troops before our attacks, shoot our soldiers, and report our locations to U.S. troops. As a result, our surprise attack was infeasible, and many of our troops were unable to achieve their objectives.”2 The attitude that all Filipinos were the enemy was widespread among the Japanese defenders. Taguchi Hiroshi, a Navy aviation mechanic who became a prisoner of war, explained to U.S. Army investigators in late March: “The enlisted men in the lower ranks, believed that, since the Filipinos indicated that they were cooperative toward Americans in their attitude and had ill feeling toward the Japanese, because prices of food and other articles during the period when we occupied the Philippines went very high . . . , higher officials ordered the destruction of Manila and the Filipinos.”
Some locals were more creative than others…
“The real heroines at San Agustin were the prostitutes, they were the ones that helped,” Gisbert declared. The Japanese had concentrated them in the Intramuros. Gisbert guessed that their numbers were in the hundreds. They were willing to serve as nurses. They were also quite good at scrounging. They could acquire clean linen, or whisky, which Gisbert used as anesthesia. All of which suggests that they had a way of influencing Japanese supply officers.
Even as American soldiers were getting killed, MacArthur refused to let them fight effectively (i.e., by using artillery) because he doesn’t want his former home trashed:
The general was genuinely horrified by what was unfolding in Manila, and seemingly unable to process it. “MacArthur was shattered by the holocaust,” Lieutenant Paul P. Rogers, the headquarters typist, observed. Everything he had done to spare Manila in 1941 was being undone by his own troops, and the major coup of taking the city intact with its port facilities undamaged was falling apart in front of him. Admitting to that kind of setback was not in him. Suddenly the general and his command had a vested interest in making sure there was as little coverage of Manila—positive or negative—as possible. A press report that declared, “Manila is dying” set him off. MacArthur ordered Diller to block any usage of that phrase. He also ordered the units under his command to refrain from using artillery in the city. “That was most unlike the General, who prided himself on winning victories with minimum loss of life,” Diller recalled.
Eventually the subordinate officers wear MacArthur down:
He appointed a three-man committee to talk with MacArthur about the artillery restrictions. After listening to the three, MacArthur, despite his vehement and emotional initial response changed course completely. His subordinates were making it clear that they were not only taking heavy losses, but at rates they could not sustain. With reporters now in the mix, he could ignore that consideration only so long. He removed all the limits on both the artillery and on the media. His public relations man was happy: “They did start using artillery, and it all worked out just exactly the way I wanted it to.” The removal of restrictions on artillery was the third major event that shaped the battle for Manila. Despite their reputation as being a bunch of “yes men,” the staff had pushed back against the general and gotten him to reverse himself. Robert S. Beightler was happy with this decision: “From this point on, we really went to town.” Beightler was advocating any means which he believed would speed up the tempo of combat and save both American and Filipino lives. After the battle ended, he reported to Krueger: “the fantastic defenses of small pockets of resistance which had been isolated required the employment of all available weapons.” Some of this argument is rather weak. The infantry used indirect fire as a crutch to avoid close combat. The problem: it resulted in the deaths of thousands of civilians. Figuring the exact numbers killed in Manila is a tricky business. It seems
Full post, including comments