Fordlandia: The Rise and Fall of Henry Ford’s Forgotten Jungle City, by Greg Grandin, is on an always-timely subject: grand plans of rich scientists and technocrats encountering nature and human nature.
The subject of the book is Henry Ford’s attempt to bring the benefits of American management to rubber cultivation in the Brazilian Amazon. The resulting town, Fordlandia, still exists, possibly home to as many as 3,000 people. The endeavor was begun in 1928 based on a foundation of false premises, the worst of which was that rubber prices would rise dramatically. There was a lot of enthusiasm for the idea, though, even beyond Ford’s offices:
“If the machine, the tractor, can open a breach in the great green wall of the Amazon jungle, if Ford plants millions of rubber trees where there used to be nothing but jungle solitude,” wrote a German daily, “then the romantic history of rubber will have a new chapter. A new and titanic fight between nature and modern man is beginning.” One Brazilian writer predicted that Ford would finally fulfill the prophecy of Alexander von Humboldt, the Prussian naturalist who over a century earlier said that the Amazon was destined to become the “world’s granary.”
Time reported that Ford intended to increase its rubber planting every year “until the whole jungle is industrialized,” cheered on by the forest’s inhabitants: “soon boa constrictors will slip down into the jungle centers; monkeys will set up a great chattering. Black Indians armed with heavy blades will slash down their one-time haunts to make way for future windshield wipers, floor mats, balloon tires.” Ford was bringing “white man’s magic” to the wilderness, the Washington Post wrote, intending to cultivate not only “rubber but the rubber gatherers as well.”
(Humboldt was a genius, but we can’t win them all! See Humboldt Biography: Climate Change Alarmism Not New.)
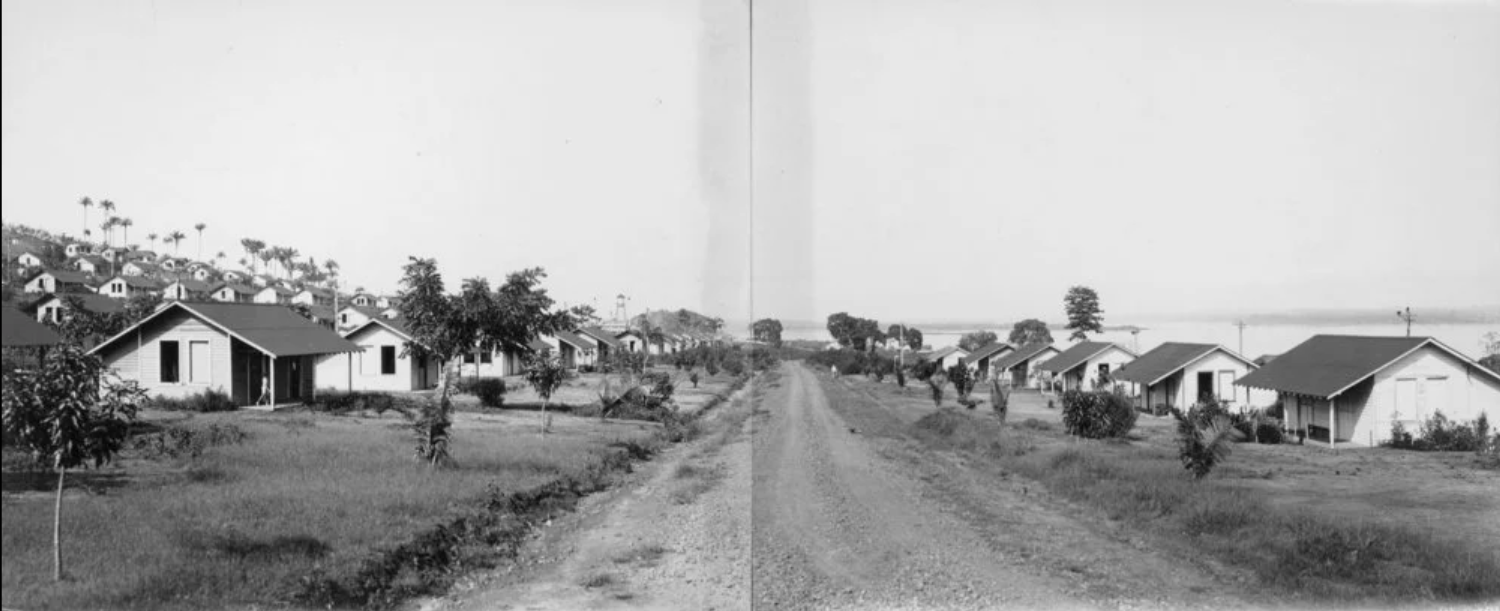
The city that Ford built was 18 hours by boat, both then and now, from urban civilization.
Why cultivate rubber in the Amazon? The European colonial powers took the rubber tree seeds and set up plantations in Asia, far away from the pests that had evolved along with the trees in the Amazon. Africa was another possibility, in terms of climate, but Ford rejected this idea:
Latex, thought Liebold, the American-born son of German Lutheran parents, should be cultivated “where the people themselves have reached a higher state of civilization.” Ford’s secretary decided that this ruled out Liberia, a country “composed entirely of Negroes whose mentality and intellectual possibilities are quite low.” “Rubber should be grown where it originated,” Liebold concluded. And that meant the Amazon.
How was it done before in the Amazon?
Hevea brasiliensis can grow as high as a hundred feet, standing straight with an average girth, at breast height, of about one meter in diameter. It’s an old species, and during its millennia-long history there likewise evolved an army of insects and fungi that feed off its leaves, as well as mammals that eat its seeds. In its native habitats of Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, and Ecuador, it best grows wild, just a few trees per acre, far enough apart to keep bugs and blight at bay; would-be planters soon learned that the cultivation of large numbers of rubber trees in close proximity greatly increased the population of rubber’s predators. The extraction and processing of latex, therefore, was based not on developing large plantations or investing in infrastructure but rather on a cumbersome and often violent system of peonage, in which tappers were compelled to spread out through the jungle and collect sap.
Tappers, known as seringueiros, lived scattered along the river, sometimes with their families but often alone, with their huts located at the head of one or two looped rubber trails that ran a few miles, connecting between a hundred and two hundred trees. In the morning, starting before sunrise, when the latex flowed freest through the thin vessels that run up the tree’s bark, the tapper would make his first round, slashing each Hevea with diagonal cuts and then placing tin cans or cups to catch the falling sap. After lunch, and a nap to escape the worst of the heat, the seringueiro made a second round to collect the latex. Back at his hut, he smoked it on a spit over an earthenware oven fired by dampened palm nuts, which produced a toxic smoke that took its toll on tapper lungs, until it formed a black ball of rubber, weighing between seventy and ninety pounds. He then brought the ball to a trading post, handing it over to a merchant either as rent for the trails or to pay off goods purchased on credit.
Americans in the 1920s didn’t have access to as much #Science as we do so they failed to realize that being isolated in an apartment for a year or more is actually the best possible thing for a human …
The workers went months without seeing other human beings, [Carl D. LaRue, a botanist from U. Michigan] said. “The loneliness is appalling.”
Transitioning these lonely natives to the American system would turn them into good Americans:
With a surety of purpose and incuriosity about the world that seems all too familiar, Ford deliberately rejected expert advice and set out to turn the Amazon into the Midwest of his imagination. “What the people of the interior of Brazil need,” he declared at the outset of the project, “is to have their economic life stabilized by fair returns for their labor paid in cash and their mode of living brought up to modern standards in sanitation and in prevention and cure of disease.”
This was a twist on an idea dating back at least to 1850, when Matthew Fontaine Maury, one of the greatest American scientists of his day, proposed transporting the southern plantation economy to the Amazon:
The question Maury asked was whether the Amazon would “be peopled with an imbecile and an indolent people or by a go ahead race that has the energy and enterprise equal to subdue the forest and to develop and bring forth the vast resources that lie hidden there.”
As it turned out, even back in Michigan, Ford had to go to extraordinary lengths to control worker behavior:
But high wages alone were not enough to ensure either factory-floor efficiency or individual responsibility. A better salary could just lead to quicker dissipation through gambling, drinking, and whoring. There was no shortage of temptations in iniquitous Detroit. There were more brothels in the city than churches, and workers often lived crowded in fetid slums, in flophouses that fronted for gambling halls, bars, and opium dens. So Ford conditioned his Five Dollar Day plan with the obligation that workers live a wholesome life.
And to make sure they did, the carmaker dispatched inspectors from his Sociological Department to probe into the most intimate corners of Ford workers’ lives, including their sex lives. Denounced as a system of paternal surveillance as often as it was lauded as a program of civic reform, by 1919 the Sociological Department employed hundreds of agents who spread out over Dearborn and Detroit asking questions, taking notes, and writing up personnel reports. They wanted to know if workers had insurance and how they spent their money and free time. Did they have a bank account? How much debt did they carry? How many times were they married? Did they send money home to the old country? Sociological men came around not just once but two, three, or four times interviewing family members, friends, and landlords to make sure previous reports of probity were accurate. They of course discouraged drinking, smoking, and gambling and encouraged saving, clean living habits, keeping flies off food, maintaining an orderly house, backyard, and front porch, and sleeping in beds. They also frowned on the taking in of boarders since, “next to liquor, dissension in the home is due to people other than the family being there.”
(Henry Ford never imagined groups of unrelated roommates being locked into their apartments for a year or two by state governors!)
Immigrants received additional training:
And though ecumenical in his hiring practices, Ford still charged his Sociological Department with Americanizing immigrants, conditioning ongoing employment on their attending English and civic classes. These courses were intentionally mixed by race and country so as to “impress upon these men that they are, or should be, Americans, and that former racial, national, and linguistic differences are to be forgotten.” Commencement from the Ford school had the graduating workers, regaled in their native dress, singing their national songs and dancing their folk dances and climbing up a ladder to enter a large papier-mâché “melting pot.” On the stage’s backdrop was painted an immigrant steamship, and as Ford teachers stirred the pot with long ladles the new amalgamated Americans emerged in “derby hats, coats, pants, vests, stiff collars, polka-dot ties,” singing “The Star-Spangled Banner.”
The Fordlandia project was predicated on a sweetheart import/export tax deal with the Brazilian government that was repudiated by later-elected politicians. Even if the core agricultural ideas had panned out, the world market for rubber and the tax environment in Brazil would likely have caused the project to fail. The local labor force also did not respond as Ford had hoped.
Rather than a midwestern city of virtue springing from the Amazon green, local merchants set up thatched bordellos, bars, and gambling houses, turning Fordlandia into a rain forest boomtown.
Similarly, when Oxholm did manage to shut down a few bordellos and bars, the proprietors simply set up shop on an island just off Fordlandia’s banks, building their brothels on stilts because the island was half wetlands and prone to floods. It was ironically dubbed the “Island of Innocence” since, as Eimar Franco put it, “no one on it was innocent.”
He also had to deal with the employees who had contracted venereal diseases, running at a rate of about nine a month, in the camp’s bordellos.
Once the workers got hold of cash wages, assuming that they didn’t spend it all in the bars and bordellos, they didn’t want to stay on the plantation after they’d earned enough to support themselves and/or their families for a year. The labor force ultimately riots and destroys most of the town, until eventually the Brazilian military shows up.
Why could drive folks in the verdant jungle to a mostly peaceful protest?
Metal roofs lined with asbestos, chosen by Ford engineers to repel the sun’s rays, in fact kept heat in. The “workers’ houses were hotter than the gates of hell,” recalled a priest who ministered in Fordlandia, “because some faraway engineer decided that a metal roof was better than something more traditional like thatch.” They were “galvanized iron bake ovens,” said Carl LaRue, commenting on Fordlandia’s foibles years later. “It is incredible that anyone should build a house like that in the tropics.”
As in the U.S. today, once babies showed up the parents looked for someone else to pay for their care:
Hundreds of babies were born each year in Fordlandia, creating a whole new set of problems for its managers. Amazon residents were used to giving birth at home under the care of a midwife. Ford doctors frowned on the practice, yet did not want to tie up hospital beds for obstetrics. So they didn’t push the issue until a woman died in childbirth in late 1931. From then on, medical and sanitation squads added a new responsibility to their ever growing list, as they checked women for pregnancy and made sure no illicit midwifery was taking place.
Once born, children needed care. Dr. McClure had hopes that Dearborn chemists would soon find a “satisfactory substitute for cow’s milk with soy bean milk” that could be used to feed infants and toddlers. But until then, Fordlandia’s hospital distributed Borden’s Klim, a powdered whole milk, to new mothers. The staff quickly learned that utensils had to be provided as
Full post, including comments