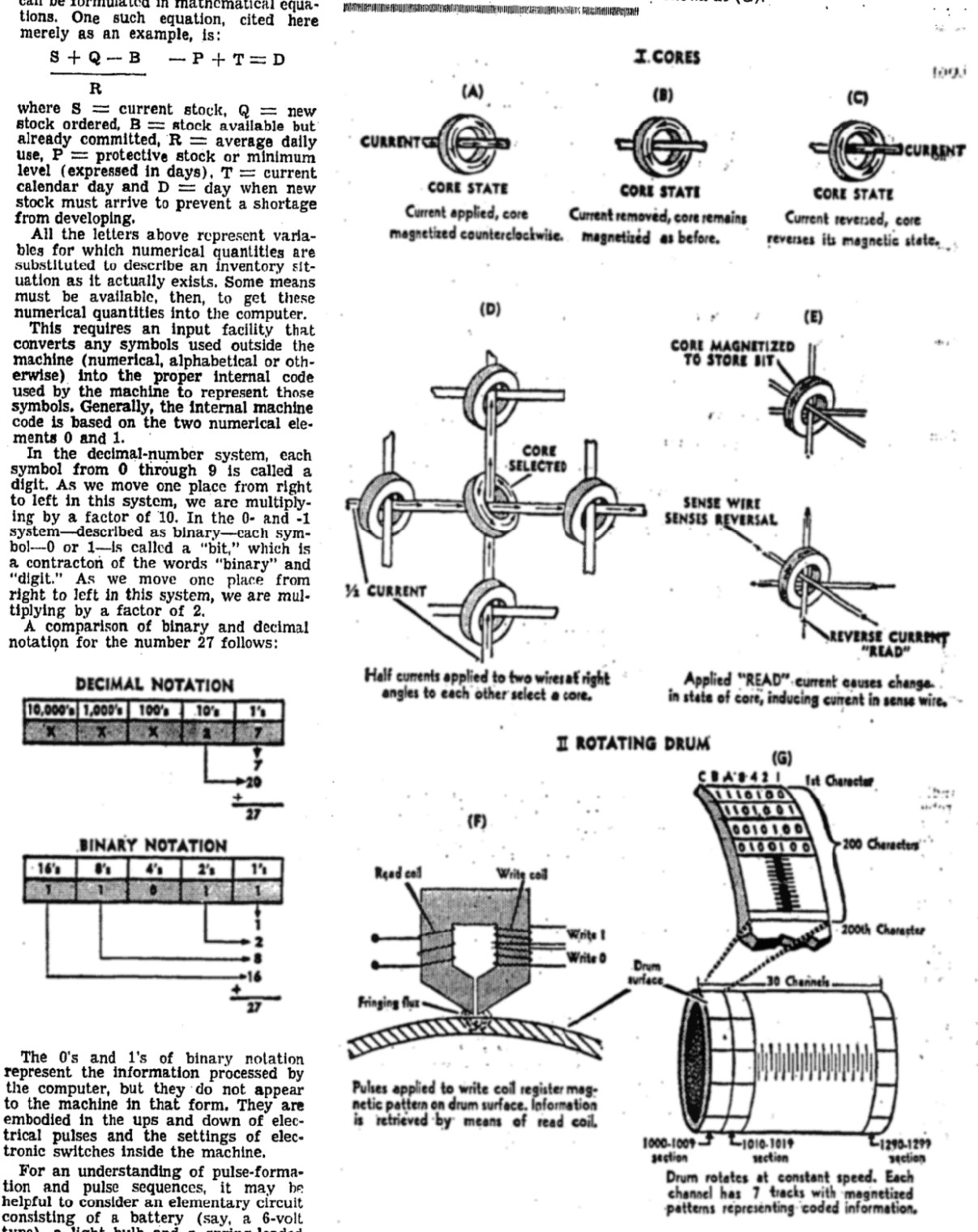
Happy Patriots’ Day
If you’re in Boston enjoying healing legal cannabis today, you can thank the traitors who rebelled against legitimate British rule in 1775 (marijuana is strictly illegal in the U.K.).
How did George III see the “patriots”? The Last King of America: The Misunderstood Reign of George III (Andrew Roberts) quotes the King writing in 1782:
I cannot conclude without mentioning how sensibly* I feel the dismemberment of America from this empire, and that I should feel miserable indeed if I did not feel that no blame on that account can be laid at my door, and did not also know that knavery seems to be so much the striking feature of its inhabitants that it may not in the end be an evil that they become aliens to this kingdom.
Good riddance to bad traitors, in other words!
Just 15 years before the Revolutionary War started, folks in Boston loved George III.
The widespread celebrations of George’s accession [in 1760] were particularly strong in Boston, capital of the King’s loyal Massachusetts Bay Colony. As the proclamation was read in which Boston acknowledged ‘all faith and constant obedience’ to the new King ‘with all hearty and humble affection’, the crowd shouted ‘Huzzah!’, militiamen fired three volleys, cannon from the harbour fort boomed and the town was illuminated in the traditional celebratory manner by placing candles in the windows of houses. The exertions Britain was making in blood and treasure to protect her American imperial brethren from incursions over the previous six years of what was then known as the French and Indian War were greatly appreciated. ‘I have been here about sixteen years,’ a Bostonian noted, ‘and I don’t know of one single man but would risk his life and property to serve King George the Third.’
Aside from marijuana laws, how has the U.S. diverged from the U.K. since 1775?
The U.S. has borrowed much more, as a percentage of GDP, than the British. What did George III have to say about that?
In one respect, however, George was not exaggerating: Britain’s ‘present load of debts’ amounted to over £74 million in 1753, to £77.8 million in 1758 and to £82.8 million in 1759, prompting a deep concern in Parliament over the nation’s creditworthiness, and reaffirming those fears in George that had been planted by Bute’s teachings and his father’s political testament. George wrote several essays on the subject in the second half of the 1750s, which in total covered no fewer than 557 pages. For the young Prince, revenue and expenditure profoundly affected national power and prosperity, and ‘to know this is the true essential business of a king’. The seriousness with which he and Bute approached this subject was no mere intellectual exercise; it was a blueprint for what they believed needed to be done about the economy once George became king and Bute his Prime Minister.
George’s conception of economics was staunchly conservative. He dreamed not of conquering great territories such as Canada and India, but rather of redeeming the National Debt and leading a great, unleveraged trading nation which would be ‘the residence of true piety and virtue’. His essays articulate his belief that the establishment of the Debt, in the reign of William III and Mary, had emerged from the cowardice of politicians in borrowing for William’s wars rather than incurring unpopularity by increasing taxation, which he characterized as a willingness ‘to live and die without the least regard to posterity, a way of thinking now become fatally prevalent’. As he wrote elsewhere, ‘The world ever produces wrong-headed individuals who would rather pay £10 imperceptibly than £4 out of their pockets at once.’ If there was a specific period when George conceived his low opinion of politicians for their short-termism, factiousness and pusillanimity – a general view that was to last throughout his reign and cause him a good deal of trouble – it was when he studied in detail the way the National Debt had ballooned in the six decades after the 1690s.
George likened the Whig governments’ behaviour in allowing this to happen to ‘a young spendthrift who eagerly compounds for a present convenience at the expense of any future encumbrance, however burdensome or reproachful’. Economics, for George, was profoundly moral. He denounced the first national lottery, of 1694, as ‘a most pernicious precedent, too often made use of since, as it serves not only to excite, but even authorize, a spirit of gaming in every man who is able to raise a few pounds, though perhaps at the expense of his morals, credit and character’.
(regarding this last point against state-sponsored gambling, see also If inequality is bad, why does the government run Powerball?)
The British thought that Europeans had stolen enough land from the Native Americans. The Patriots disagreed.
On 7 October 1763, possibly in part as a result of the Cherokee embassy the previous year, the British government made a decision that was to become one of the major causes of the loss of the North American colonies. Severely rattled by the still-ongoing Pontiac uprising in the Ohio Valley, and conscious of the promises made to Native American tribes that had supported Britain in the Seven Years War, Lord Halifax (who for thirteen years had been First Lord of Trade and Plantations) issued a proclamation to prevent the American colonists’ westward settlement. The whole continent to the west of a Proclamation Line, running from the Great Lakes down to the Gulf of Mexico and along the western slopes of the Appalachian Mountains, would be one gigantic Native American reserve where no American colonial settlement would be permitted. There was even an order for settlers then on the western side of the Line ‘forthwith to remove themselves’. This was a major obstacle to the expansion of American wealth and growth. Now, far from viewing the twenty battalions of British troops as being for their own protection, the colonists saw them as enforcing a new policy of boxing them into the seaboard colonies and preventing expansion from ocean to ocean.
George had distributed large silver friendship ‘peace medals’ to the chiefs of Native American allies and trading partners during the Seven Years War and was not willing to betray them. Yet the exponential population growth of the thirteen colonies meant that Americans were looking to move westwards across the continent. In the almost inevitable struggle between the American colonists and the Indigenous Nations on the other side of the Appalachians, Britain had attached herself to what would be the losing side for the short-term gain of the fur trade. It was now very much in American colonists’ interests that the taxes to pay for the British troops should not be raised, so that the Proclamation Line could not be policed. The first and most obvious losers from the Proclamation were those speculators who had intended to develop the land between the Allegheny Mountains and the Mississippi, among whom were Benjamin Franklin, Patrick Henry, the Lee family and George Washington. In September 1763, Washington and nine other speculators had launched the Mississippi Land Company, with the intention of claiming 2.5 million acres in the Ohio Valley, covering what is today Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee.
(See George Washington, Mules, and Donald Trump: “the author reminds us that real estate speculator-to-president is not an entirely new path”)
Slavery was a substantial difference between England and what became the U.S.
Forty-one of the fifty-six signatories to the Declaration owned slaves at one point in their lives, and Thomas Hutchinson wrote that he ‘could wish to ask the delegates of Maryland, Virginia and the Carolinas how their constituents justify the depriving more than an hundred thousand Africans of their right to liberty and the pursuit of happiness’.
So… we fought for the rights to smoke dope, keep slaves, borrow and spend wildly, and steal land from the Native Americans.
Full post, including comments